Electrical Insulation Properties of Low Voltage Conical Insulators
Blog | Phòng tin tức | Th1 16,2026
Giới thiệu
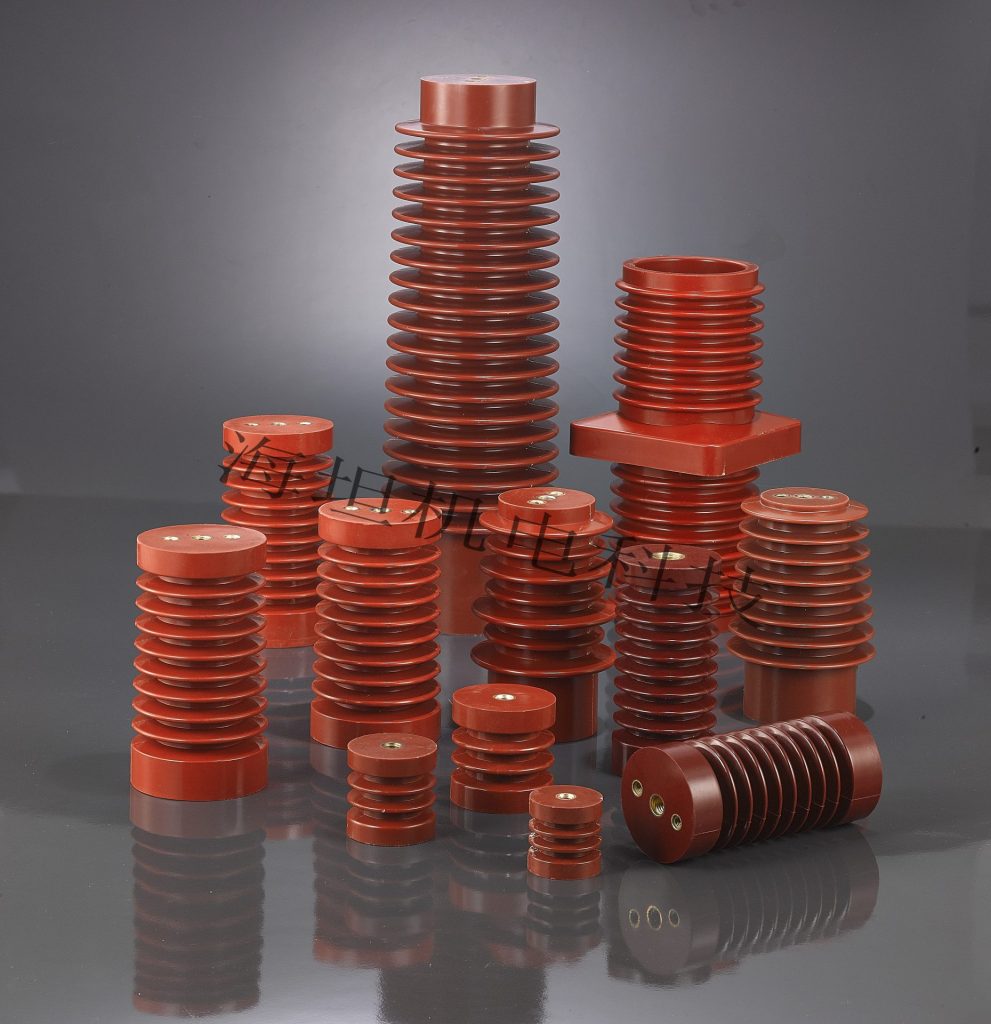
In low voltage power distribution systems, insulation performance is one of the most critical factors for safe and reliable operation. Among various insulator types, low voltage conical insulators are widely used in switchgear, motor control centers, and distribution panels due to their compact design, mechanical strength, and excellent electrical insulation properties.
What Are Low Voltage Conical Insulators?
Low voltage conical insulators are rigid insulating components designed to support busbars, conductors, or terminals while electrically isolating them from grounded structures. Their conical shape provides several advantages, including increased creepage distance, better voltage distribution, and stable mechanical support.
They are typically used in systems operating at voltages below 1,000 V and are commonly made from materials such as:
DMC (Hợp chất đúc bột) – high mechanical and electrical strength
sứ – traditional material with high dielectric strength
Composite materials – fiberglass core with insulating coatings for specific applications
Key Electrical Insulation Properties
Độ bền điện môi
Dielectric strength is the maximum voltage that an insulator can withstand without breaking down. Low voltage conical insulators are designed to resist high electrical stress between the live conductor and grounded support.
High dielectric strength prevents arcing and flashover
Ensures safety under transient overvoltage conditions
Supports reliable operation in compact panel designs
Khoảng cách đường dây
Creepage distance is the shortest path along the insulator surface between conductive parts at different potentials. The conical design enhances creepage distance without increasing overall size.
Improves resistance to surface tracking and leakage currents
Especially important in humid or dusty environments
Reduces the risk of short circuits and equipment failure
Surface Insulation Resistance
The surface insulation resistance measures how well the insulator resists leakage currents along its surface. Low voltage conical insulators maintain high surface resistance even in polluted or damp conditions.
Prevents gradual insulation degradation
Minimizes maintenance and cleaning requirements
Enhances long-term reliability of panels and switchgear
Arc and Tracking Resistance
Low voltage conical insulators are designed to resist localized arcing and surface tracking:
Materials like DMC or composite coatings provide high arc resistance
Conical shape reduces the likelihood of arcing paths forming
Improves overall electrical safety in industrial or outdoor installations
Thermal and Electrical Stability
Electrical insulation properties must remain stable under temperature variations and load conditions. Low voltage conical insulators:
Maintain dielectric strength under thermal stress
Resist insulation breakdown during short-term overloads
Ensure consistent performance across varying operating conditions
Why Electrical Insulation Properties Matter
The electrical insulation properties of low voltage conical insulators directly affect:
System safety – preventing shocks and short circuits
Equipment reliability – avoiding flashover and downtime
Panel compactness – enabling high-density layouts without compromising insulation
Chi phí bảo trì – reducing the frequency of cleaning and replacement
Selecting high-quality insulators with superior insulation properties ensures both long-term system stability and personnel safety.
Applications of Low Voltage Conical Insulators
Low voltage conical insulators are widely used in:
Switchgear and distribution panels – supporting busbars and live parts
Motor Control Centers (MCCs) – isolating terminals and conductors
Industrial control panels – compact and high-density installations
Hệ thống năng lượng tái tạo – low voltage DC and AC connections
In all these applications, electrical insulation properties are critical for preventing faults and maintaining continuous operation.
Phần kết luận
Low voltage conical insulators are not just mechanical supports—they are key electrical insulation components in low voltage systems. Their dielectric strength, creepage distance, surface resistance, and arc resistance ensure safe operation, long-term reliability, and reduced maintenance requirements.
By understanding and prioritizing these electrical insulation properties, engineers and system designers can make smarter choices for low voltage panels, switchgear, and industrial electrical systems.
Câu hỏi thường gặp
1. What is the main function of a low voltage conical insulator?
The primary function is to support busbars or conductors mechanically while electrically isolating them from grounded structures, ensuring safe current flow and preventing short circuits or flashover in low voltage systems.
2. How does the conical shape improve insulation performance?
The conical design increases creepage distance along the surface without increasing overall size, reducing the risk of leakage currents, surface tracking, and flashover, especially in humid or polluted environments.
3. What materials are commonly used for low voltage conical insulators?
DMC (Hợp chất đúc bột) – high dielectric strength and mechanical durability
sứ – traditional material with excellent dielectric properties
Composite materials – fiberglass core with insulating coatings for enhanced arc and tracking resistance
4. What is dielectric strength, and why is it important?
Dielectric strength is the maximum voltage an insulator can withstand without breakdown. High dielectric strength prevents arcing and electrical failure, ensuring safety for both equipment and personnel.
5. How do low voltage conical insulators resist surface leakage and tracking?
They maintain high surface insulation resistance through material selection and conical geometry, which prevents leakage currents and reduces maintenance needs in dusty or humid environments.
6. Can low voltage conical insulators handle thermal stress?
Yes. They are designed to maintain dielectric and mechanical stability under temperature variations and short-term overloads, ensuring reliable insulation performance over time.
--- KẾT THÚC ---
© Bản quyền 2024 Công ty TNHH Công nghệ Cơ điện Haitan Trung Quốc. Mọi quyền được bảo lưu.HỖ TRỢ BỞI: JUNJ Chính sách bảo mật


 Email:
Email:  Số 20 đường Lingyun, Đông Phong
Số 20 đường Lingyun, Đông Phong 
