Towards Smart Grid: Development Trends and Standardization Process of DMC Insulators
Introduction
As global energy systems move toward the era of Smart Grids, the demand for reliable, efficient, and sustainable insulation materials has never been higher. In this transformation, DMC Insulators (Dough Moulding Compound Insulators) are emerging as one of the most important components in modern electrical systems.
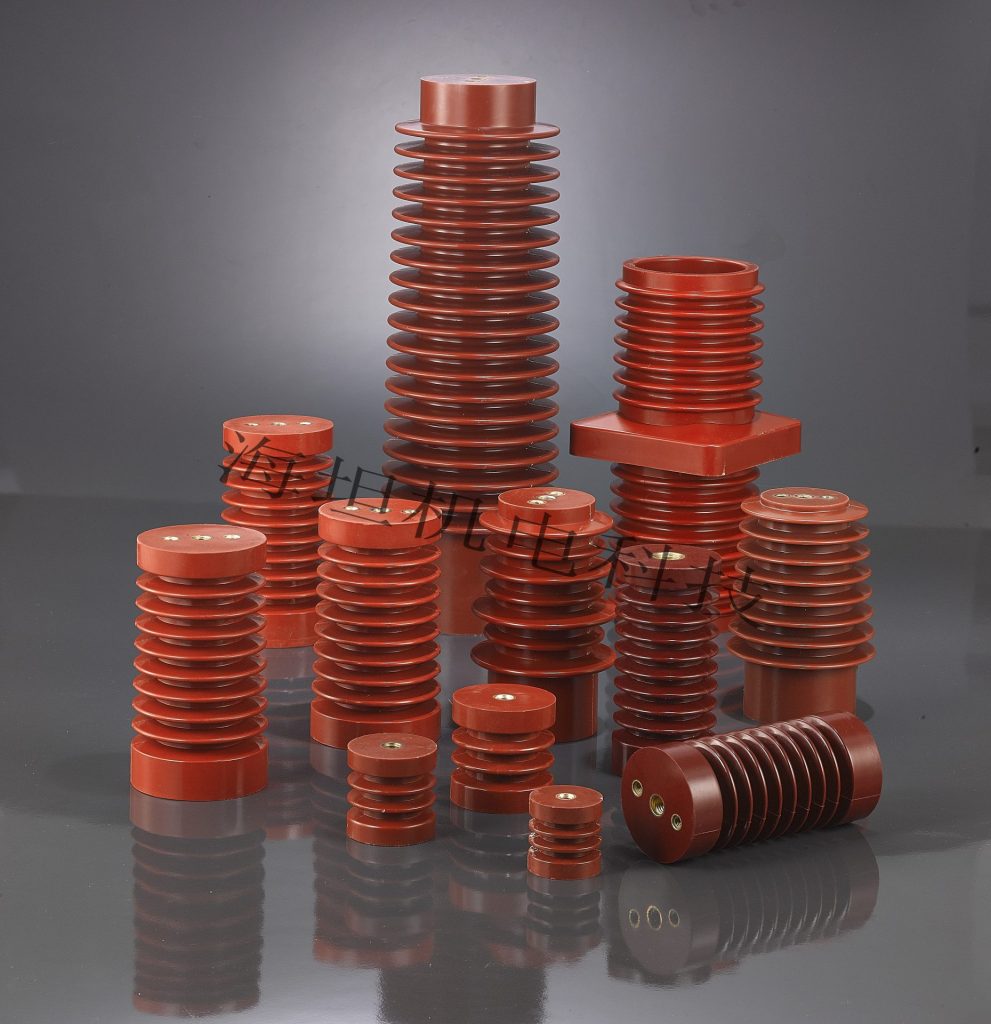
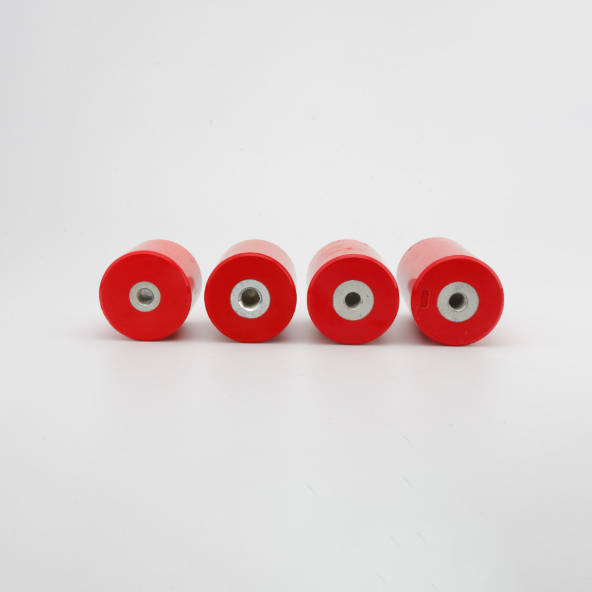
A DMC Electrical Insulator combines mechanical strength, electrical performance, and environmental resistance, offering a balance of safety and efficiency in power distribution networks. From low-voltage switchgear to smart metering systems, these insulators play a vital role in ensuring system stability and reliability.
This article explores the development trends, manufacturing processes, and standardization journey of DMC Insulators — revealing how this advanced material technology supports the Smart Grid revolution.
Material and Structural Advantages of DMC Insulators
Composition of DMC: unsaturated polyester resin, glass fiber, and filler materials
DMC (Dough Moulding Compound) is a composite material primarily composed of unsaturated polyester resin, chopped glass fibers, and inorganic fillers. This unique combination gives DMC Insulators their outstanding structural integrity and insulation performance while maintaining dimensional stability under stress and temperature variations.
Key DMC Insulator Material Properties
A well-engineered DMC Insulator delivers:
High mechanical strength – withstands impact, vibration, and mechanical loads.
Superior electrical insulation – ensures minimal leakage current and high dielectric strength.
Thermal and moisture resistance – performs reliably in humid, high-temperature, or outdoor conditions.
These DMC Insulator Material Properties make them ideal for applications where safety and durability are critical.
Comparison with traditional porcelain and epoxy insulators
Compared to porcelain and epoxy resin alternatives, DMC Electrical Insulators offer several advantages:
Lighter weight, reducing installation and transportation costs.
Higher impact resistance, minimizing breakage during assembly.
Better surface finish, providing consistent electrical performance.
Lower production cost and easier mass manufacturing.
Role of DMC as a Sustainable Electrical Insulator Material
As industries emphasize environmental responsibility, Sustainable Electrical Insulator Materials like DMC are gaining importance. DMC’s low curing energy consumption, recyclability, and reduced reliance on mineral resources contribute to greener production and sustainable Smart Grid infrastructure.
Development Trends of DMC Insulators for Smart Grid
The evolving needs of insulation systems in Smart Grid infrastructure
Smart Grids demand intelligent, compact, and efficient insulation systems capable of handling variable loads, renewable inputs, and advanced monitoring. DMC Insulator for Smart Grid applications meet these needs through precision molding and adaptable design.
Innovative DMC Insulator Applications in Smart Grid
DMC Insulators are increasingly used in:
Smart meters for household and industrial energy management.
Low and medium-voltage switchgear systems.
Distribution transformers and control panels.
These DMC Insulator Applications in Smart Grid showcase the material’s ability to perform under high mechanical and electrical stress.
Major DMC Insulator Trends
The current DMC Insulator Trends include:
Lightweight and compact design for space-saving installations.
Modular structure for easier maintenance and scalability.
Integration with digital monitoring systems for predictive maintenance and performance tracking.
Integration of Composite Insulators in Smart Grid
The evolution of Composite Insulators in Smart Grid reflects a broader shift toward hybrid materials. DMC blends well with silicone rubber and other composites, combining structural rigidity with superior surface hydrophobicity — improving long-term reliability.
Standardization and Certification Process of DMC Insulators
Importance of DMC Insulator Standardization
DMC Insulator Standardization ensures consistent quality, safety, and interoperability across global Smart Grid projects. Without proper standards, differences in material composition and manufacturing can compromise reliability and compatibility.
Overview of current standards: IEC, ANSI, and GB/T frameworks
DMC Insulators are designed and tested according to major international frameworks, including:
IEC 60112, IEC 60243, IEC 60372 for dielectric and mechanical performance.
ANSI C29 series for electrical insulators.
GB/T 5582, GB/T 5583 for material testing in the Chinese standard system.
The impact of Standardization of Electrical Insulators
Uniform standards enable manufacturers to meet global quality benchmarks, improving international trade and system interoperability. The Standardization of Electrical Insulators also helps utilities evaluate product performance objectively.
Typical DMC Insulator Testing and Certification Process
The DMC Insulator Testing and Certification process typically involves:
Electrical performance testing
Evaluation of dielectric strength, voltage endurance, and insulation resistance to ensure safe operation under high voltage conditions.
Mechanical and environmental durability tests
Verification of tensile strength, impact resistance, and performance under extreme temperature or humidity.
Thermal aging and flame resistance evaluations
Testing under accelerated aging conditions to confirm long-term stability and flame retardancy.
Example of DMC Insulator Performance Standards
For example, IEC 61109 and IEC 62217 define performance requirements and routine tests for composite insulators used in power distribution — both applicable to DMC-based designs.
Manufacturing and Quality Control in DMC Insulator Production
Overview of DMC Insulator Manufacturing Process
The DMC Insulator Manufacturing process includes:
Molding: compressing DMC material into pre-heated molds.
Curing: hardening under controlled temperature and pressure.
Surface finishing: trimming, coating, and inspection.
Manufacturing precision ensures consistent performance
Precision in temperature, pressure, and curing time guarantees the uniform density and dielectric properties of each Electrical DMC Insulator.
Adoption of automation and IoT monitoring
Modern factories integrate IoT systems for real-time monitoring of temperature and pressure during molding. Automated inspection systems also detect micro-defects that might affect insulation performance.
Smart manufacturing and quality assurance for Smart Grid Insulation Design
These advancements align with Smart Grid Insulation Design principles — producing high-quality, traceable, and performance-verified insulation components that meet the needs of intelligent power systems.
Benefits and Future Outlook of DMC Insulators in Smart Grids
Summary of DMC Insulator Benefits and Advantages
Key DMC Insulator Benefits and Advantages include:
Excellent dielectric and mechanical properties.
Lightweight, compact structure for easy installation.
Low water absorption and superior environmental durability.
Cost-effective mass production and consistent quality.
Long-term economic and maintenance benefits
Over the equipment’s lifespan, DMC Insulators require minimal maintenance and replacement, reducing downtime and operational costs compared to porcelain or epoxy insulators.
Future potential of DMC in Smart Grid Insulation Components
As Smart Grids expand globally, DMC Insulators will continue to be key Smart Grid Insulation Components, supporting energy efficiency, automation, and digital monitoring integration.
Supporting sustainable and intelligent energy networks
With their balance of sustainability, performance, and cost, DMC Insulators are helping utilities build more intelligent and environmentally responsible power systems for the future.
FAQ
Q1: What makes DMC Insulators suitable for Smart Grid applications?
They provide superior insulation, mechanical strength, and resistance to harsh environmental conditions while supporting compact and modular designs ideal for smart equipment.
Q2: How do DMC Insulators differ from epoxy or ceramic insulators?
They are lighter, more impact-resistant, and easier to produce in large quantities — without compromising electrical performance.
Q3: Are DMC Insulators environmentally friendly?
Yes. Their production requires less energy, and DMC can be partially recycled, aligning with sustainable manufacturing goals.
Q4: What standards should DMC Insulators comply with?
IEC, ANSI, and GB/T standards — particularly IEC 60243, IEC 60372, and ANSI C29 — are commonly applied to ensure safety and reliability.
Conclusion
The shift toward Smart Grids demands a new generation of reliable, efficient, and sustainable insulation technologies. DMC Insulators perfectly embody these requirements through their advanced material properties, standardized quality, and smart manufacturing adaptability.
By following strict standardization processes and embracing technological innovation, DMC Insulators are set to become a cornerstone in the future of Smart Grid insulation design, helping create a safer, greener, and more connected energy world.
--- END ---
© Copyright 2024 China Haitan Electromechanical Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.SUPPORT BY:JUNJ Privacy Policy


 E-mail:
E-mail:  No. 20 Lingyun Road, Dongfeng
No. 20 Lingyun Road, Dongfeng 
