The Indispensable Role of Flame Retardant and High Temperature Resistance in Insulators
In modern electrical systems, insulators are more than just components for electrical isolation; they are critical guardians that must maintain their integrity under diverse and often harsh conditions. Among their most vital attributes are flame retardancy and high temperature resistance, which are core indicators of an insulator’s quality, reliability, and safety. This article will delve into why these properties are so crucial and guide you on selecting the right insulators for your specific applications.
Why Flame Retardancy is Non-Negotiable for Insulators
Electrical faults often generate intense heat or sparks. If the insulating material itself is flammable, it poses a significant fire hazard. The flame retardant property of an insulator ensures that upon exposure to flame or high temperatures, it will self-extinguish or, at the very least, not contribute to the spread of fire.
- 1.1 Understanding Flame Retardancy
- Brief explanation of how flame retardant materials work.
- Discussion of common industry flame retardancy standards, such as the UL 94 V-0 rating, and their practical implications.
- Keyword Integration: Emphasize how high-quality BMC Insulator and SMC Insulator achieve these stringent flame retardancy requirements through specialized formulations and additives.
- 1.2 Impact of Flame Retardancy on Electrical Systems
- Fire Containment: In the event of a short circuit or other electrical fault, flame retardant insulators effectively limit the ignition source, protecting surrounding equipment and personnel.
- Reduced Smoke and Toxicity: Superior flame retardant materials produce less smoke and lower toxicity when exposed to fire, providing crucial time for evacuation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many national and international electrical safety regulations mandate the use of materials that meet specific flame retardancy standards.
High Temperature Resistance: Enduring the Heat
Electrical equipment continuously generates heat during operation, and under high current loads or overload conditions, temperatures can rise sharply. If an insulator cannot withstand these elevated temperatures, its physical and electrical properties will rapidly degrade, leading to insulation failure.
- 2.1 Defining High Temperature Resistance
- Explanation of key terms like an insulator’s “heat deflection temperature” and “continuous operating temperature.”
- How these parameters directly influence the long-term reliability and lifespan of an insulator.
- 2.2 Material Selection for High Temperature Performance
- Overview of common materials used in the manufacturing of high-temperature resistant insulators, such as BMC (Bulk Molding Compound) and SMC (Sheet Molding Compound).
- Detailed explanation of how these materials, through glass fiber reinforcement and specific resin systems, provide exceptional thermal endurance.
- Keyword Integration: Highlight the application advantages of products like SMC Busbar Support Insulator and Low Voltage Standoff Insulators in high-temperature environments.
How Insulator Performance is Evaluated and Certified
Beyond simply reviewing product specifications, understanding the testing methodologies for insulators is vital. This knowledge empowers customers to make more informed and confident product selections.
- 3.1 Flame Retardancy Testing
- Glow-wire Test: Simulating the effect of overheated components within electrical equipment on insulating materials.
- Vertical Burning Test (UL 94): Assessing a material’s ability to extinguish a flame after ignition and its dripping behavior.
- Oxygen Index Test: Determining the minimum oxygen concentration required to support combustion.
- 3.2 High Temperature Resistance Testing
- Thermal Aging Test: Subjecting insulators to prolonged periods of high temperature to observe changes in mechanical and electrical properties.
- Relative Temperature Index (RTI) Test: Establishing the maximum temperature at which a material can be expected to function reliably for a specified period.
- Dielectric Strength at Elevated Temperatures: Measuring the insulating capability under thermal stress.
Why Choose Our Insulators? Your Partner in Electrical Safety
As a dedicated insulator supplier, we understand the paramount importance of flame retardancy and high temperature resistance to our customers. Our product line is meticulously designed to provide safe, reliable, and high-performance solutions for a wide range of electrical applications.
- 4.1 Our Product Advantages
- Premium Materials: All our insulators are crafted from high-grade BMC and SMC materials, undergoing rigorous selection and optimized formulation.
- Strict Performance Standards: Our products strictly adhere to international flame retardancy and temperature resistance standards, including UL 94 V-0, and are backed by comprehensive performance reports.
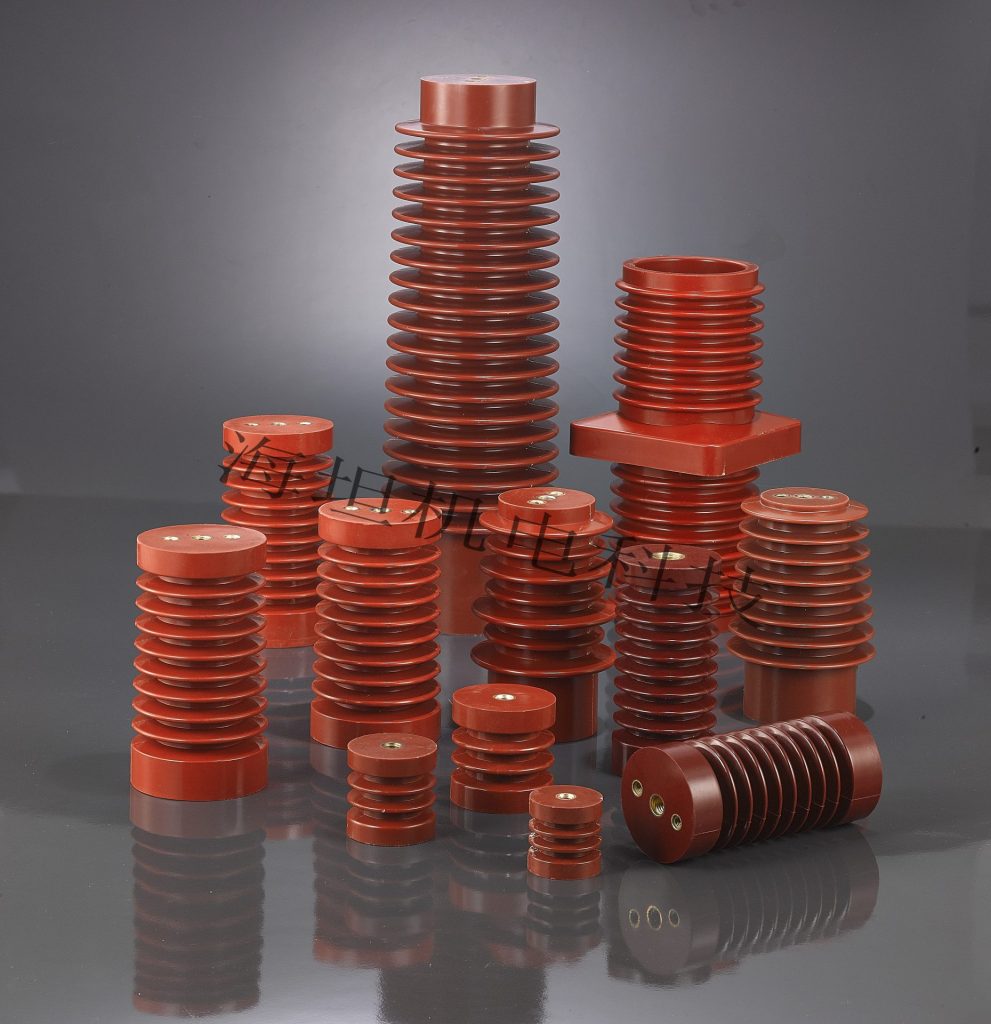
- Versatile Applications: Our diverse product range covers everything from SM Insulator to Low Voltage Insulator, meeting the demands of switchgear, control panels, distribution boxes, and various industrial electrical systems.
- 4.2 Featured Product Recommendations
- SM Busbar Support Insulators: Engineered to provide robust support and reliable insulation for busbars, maintaining stability even under high temperatures and short-circuit currents.
- Low Voltage Standoff Insulators: Ideal for low-voltage distribution systems, offering superior electrical isolation and mechanical strength to ensure safe and continuous equipment operation.
Conclusion
The flame retardant and high temperature resistant properties of insulators are not merely optional features; they are foundational elements that ensure the safe and reliable operation of your entire electrical system. When selecting insulators, it is imperative to prioritize these characteristics alongside voltage and mechanical load capabilities. We are committed to providing top-quality insulator products that safeguard your electrical infrastructure.
Should you have any questions about our products or require customized solutions, please do not hesitate to contact us. We are here to help you make informed decisions for ultimate electrical safety and performance.
--- END ---
© Copyright 2024 China Haitan Electromechanical Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.SUPPORT BY:JUNJ Privacy Policy



 E-mail:
E-mail:  No. 20 Lingyun Road, Dongfeng
No. 20 Lingyun Road, Dongfeng 
