What Is a High Voltage Post Insulator? Definition, Structure, and Working Principle
Introduction
In high voltage power systems, safe and reliable insulation is essential for maintaining system stability and protecting equipment and personnel. Among the various insulation components used in substations and switchgear, high voltage post insulators play a critical role by providing both electrical insulation and mechanical support.
Definition of a High Voltage Post Insulator
A high voltage post insulator is a rigid insulating component designed to support and electrically isolate live conductors or busbars from grounded structures in high voltage environments. Unlike suspension or line insulators, post insulators are typically mounted vertically or horizontally on a fixed base and remain stationary during operation.
They are widely used in substations, switchgear, and busbar systems to ensure safe current flow and mechanical stability under high voltage conditions.
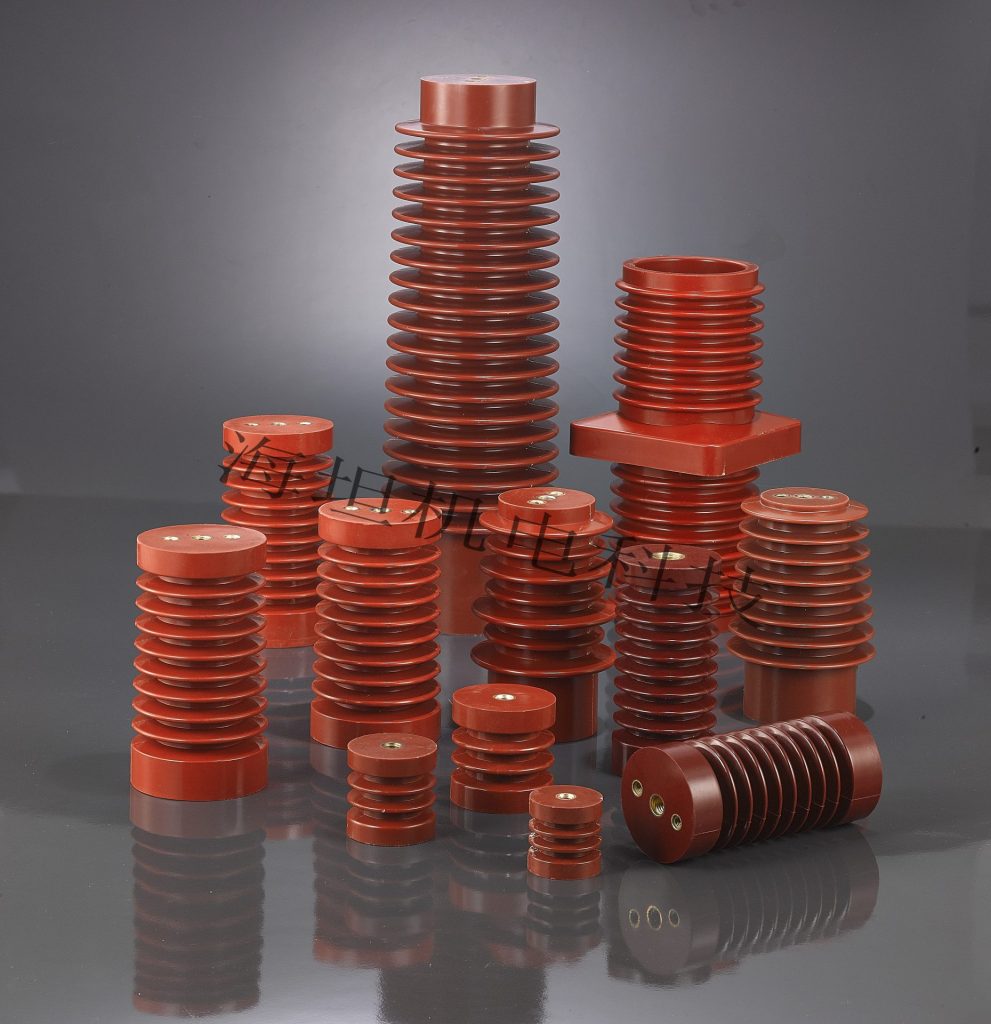
Basic Structure of a High Voltage Post Insulator
Although designs may vary depending on voltage level and application, a typical high voltage post insulator consists of the following main components:
Insulating Body
The insulating body is the core functional part of the post insulator. It is usually made from:
Porcelain
Composite materials (such as fiberglass core with silicone rubber housing)
DMC or epoxy-based materials for specific applications
This part provides high dielectric strength and determines the insulator’s creepage distance and insulation performance.
End Fittings and Mounting Hardware
High voltage post insulators are equipped with metal end fittings at the top and bottom. These fittings:
Allow secure connection to busbars or conductors
Provide firm anchoring to the supporting structure
Transfer mechanical loads safely
The fittings are typically made from galvanized steel or aluminum alloy for strength and corrosion resistance.
Shed or Rib Design (for Outdoor Insulators)
For outdoor applications, the insulating body often features sheds or ribs. These:
Increase creepage distance
Improve performance in polluted or wet environments
Reduce the risk of surface flashover
The shed design is especially important in high humidity, coastal, or industrial areas.
Working Principle of a High Voltage Post Insulator
The working principle of a high voltage post insulator is based on electrical insulation and mechanical support.
Electrical Insulation
The insulator prevents electrical current from flowing between the energized conductor and the grounded support. It achieves this by:
Providing a high-resistance insulation path
Maintaining adequate clearance and creepage distance
Preventing surface tracking and flashover
This ensures that electricity flows only along the intended conductor path.
Mechanical Support
In addition to insulation, the post insulator supports:
The weight of conductors or busbars
Mechanical forces caused by wind, vibration, or seismic activity
Electromagnetic forces during short-circuit conditions
Its rigid structure keeps the conductor in a fixed position, ensuring stable system geometry.
Applications of High Voltage Post Insulators
High voltage post insulators are widely used in:
Substations (indoor and outdoor)
High voltage switchgear
Busbar support systems
Power plants and grid interconnections
They are essential components wherever high voltage conductors must be securely supported and insulated.
Importance of High Voltage Post Insulators in Power Systems
High voltage post insulators contribute to:
Electrical safety and system reliability
Prevention of flashover and insulation failure
Stable mechanical support under normal and fault conditions
Without properly designed post insulators, high voltage systems would face increased risks of outages, equipment damage, and safety incidents.
Conclusion
A high voltage post insulator is a fundamental component in modern power systems, combining electrical insulation with mechanical strength. By understanding its definition, structure, and working principle, engineers and system designers can make better decisions when selecting insulators for substations and high voltage equipment.
Choosing the right high voltage post insulator is not just a technical requirement—it is a key factor in ensuring long-term system safety, reliability, and performance.
FAQ
1. What is a high voltage post insulator used for?
A high voltage post insulator is used to support and electrically isolate live conductors or busbars from grounded structures. It ensures safe current flow and prevents flashover or insulation failure in high voltage systems.
2. What materials are high voltage post insulators made of?
They are commonly made from:
Porcelain – traditional material with high dielectric strength
Composite materials – fiberglass core with silicone rubber housing for outdoor and polluted environments
DMC or epoxy – used in specific industrial applications for high mechanical and electrical performance
3. How does a post insulator provide electrical insulation?
The insulating body creates a high-resistance path between the conductor and the grounded support. Its design, including creepage distance and sheds, prevents surface tracking, flashover, and accidental current leakage.
4. Can high voltage post insulators support mechanical loads?
Yes. Post insulators are designed to handle:
The weight of conductors or busbars
Mechanical stress from wind, vibration, and seismic events
Electromagnetic forces during short-circuit events
This ensures the conductors remain securely in position.
5. What is the difference between a post insulator and a line insulator?
Post insulators: Used for stationary support in substations and switchgear, combining insulation and mechanical strength.
Line insulators: Used for suspension or tension on overhead power lines, often designed to hang or support cables dynamically.
6. How do sheds or ribs improve insulator performance?
Sheds or ribs increase creepage distance, which improves resistance to pollution and moisture. They reduce the risk of surface flashover, especially in outdoor environments with high humidity, coastal exposure, or industrial pollution.
--- END ---
© Copyright 2024 China Haitan Electromechanical Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.SUPPORT BY:JUNJ Privacy Policy


 E-mail:
E-mail:  No. 20 Lingyun Road, Dongfeng
No. 20 Lingyun Road, Dongfeng 
